C# Type System contains three Types , they are Value Types , Reference Types and Pointer Types. C# allows us to convert a Value Type to a Reference Type, and back again to Value Types . The operation of Converting a Value Type to a Reference Type is called Boxing and the reverse operation is called Unboxing.
Boxing is the process of converting a value type to the type object or to any interface type implemented by this value type. When the CLR boxes a value type, it wraps the value inside a System.Object and stores it on the managed heap. Unboxing extracts the value type from the object.
Boxing using code:-
The first line we created a Value Type Val and assigned a value to Val. The second line , we created an instance of Object Obj and assign the value of Val to Obj. From the above operation (Object Obj = i ) we saw converting a value of a Value Type into a value of a corresponding Reference Type . These types of operation is called Boxing.
UnBoxing using code:-
The first two line shows how to Box a Value Type . The next line (int i = (int) Obj) shows extracts the Value Type from the Object . That is converting a value of a Reference Type into a value of a Value Type. This operation is called UnBoxing.
Boxing and UnBoxing are computationally expensive processes. When a value type is boxed, an entirely new object must be allocated and constructed , also the cast required for UnBoxing is also expensive computationally.
Source code example:-
Boxing is the process of converting a value type to the type object or to any interface type implemented by this value type. When the CLR boxes a value type, it wraps the value inside a System.Object and stores it on the managed heap. Unboxing extracts the value type from the object.
Boxing using code:-
- int Val = 1;
- Object Obj = Val; //Boxing
The first line we created a Value Type Val and assigned a value to Val. The second line , we created an instance of Object Obj and assign the value of Val to Obj. From the above operation (Object Obj = i ) we saw converting a value of a Value Type into a value of a corresponding Reference Type . These types of operation is called Boxing.
UnBoxing using code:-
- int Val = 1;
- Object Obj = Val; //Boxing
- int i = (int)Obj; //Unboxing
The first two line shows how to Box a Value Type . The next line (int i = (int) Obj) shows extracts the Value Type from the Object . That is converting a value of a Reference Type into a value of a Value Type. This operation is called UnBoxing.
Boxing and UnBoxing are computationally expensive processes. When a value type is boxed, an entirely new object must be allocated and constructed , also the cast required for UnBoxing is also expensive computationally.
Source code example:-
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleDemoApp
{
class Test
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("Enter a
Integer value");
int value = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
//Boxing
implicit conversion
Object Obj = value;
Console.WriteLine("Boxing(Object/Boxed
Value) : {0}\n", Obj.ToString());
//Unboxing
explicit conversion
int num = (int)Obj;
Console.WriteLine("UnBoxing(Entered
Number Value): {0}\n", num);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
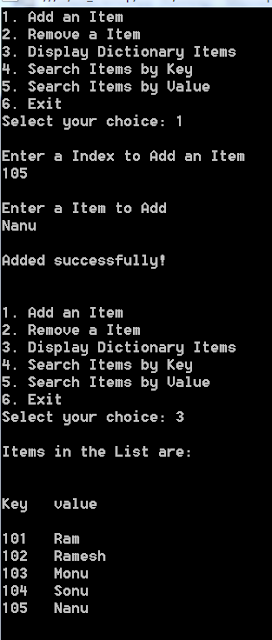
Output:-