Dictionary in c#
As Dictionary work with two type of data (one for ‘key’ and one for ‘value’), it requires both these data types to be defined at the time of initialization. Also, the namespace “System.Collections.Generic” is required for using dictionary in your application.A Dictionary class is a data structure that represents a collection of keys and values pair of data. The key is identical in a key-value pair and it can have at most one value in the dictionary, but a value can be associated with many different keys.
This class is defined in the System.Collections.Generic namespace, so you should import or using System.Collections.Generic namespace.
Syntex:-
Dictionary<KeyObject, ValueObject> DicObj = new Dictionary<KeyObject, ValueObject>();
Initialize A Dictionary Object In C#:
Dictionary<string, string> DicObj = new Dictionary<string, string>();
Methods:-
2. DicObj.Remove(index); // to Remove from Dictionary
3. DicObj.Clear(); // to Clear all Key/Values from Dictionary
// to determine the existence of Item in Dictionary
- 1Bool IsExist = DicObj.ContainsKey(index);
- Bool IsExist = DicObj.ContainsValue(item);
Traverse and display Dictionary Items:-
foreach( KeyValuePair<string, string> item in DicObj)
{
Console.Write(item.Key +" "+ item.Value);
Console.Write("\n");
}
Source code in c#:-
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleAppDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary_Operations classObj = new Dictionary_Operations();
while (true)
{
//
Console.Clear();
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("1. Add an
Item");
Console.WriteLine("2. Remove a
Item");
Console.WriteLine("3. Display
Dictionary Items");
Console.WriteLine("4. Search
Items by Key");
Console.WriteLine("5. Search
Items by Value");
Console.WriteLine("6.
Exit");
Console.Write("Select your
choice: ");
int choice = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
classObj.Add();
break;
case 2: classObj.RemoveItem();
break;
case 3: classObj.Display();
break;
case 4: classObj.SearchByKey();
break;
case 5: classObj.SearchByValue();
break;
case 8: System.Environment.Exit(1);
break;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
public class Dictionary_Operations
{
string item;
string index;
bool IsExist = false;
Dictionary<string, string> DicObj = new Dictionary<string, string>();
// Add
an Item to Dictionary
public void Add()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nEnter a
Index to Add an Item");
index = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("\nEnter a
Item to Add");
item = Console.ReadLine();
DicObj.Add(index, item);
Console.Write("\nAdded
successfully! \n");
}
//remove
an item at any given index
public void RemoveItem()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nEnter a
Index to Remove an Item");
index = Console.ReadLine();
DicObj.Remove(index);
Console.Write("\nItem
Removed successfully!: \n");
}
//Search
Item by using Key
public void SearchByKey()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nEnter a
Index to Search an Item");
index = Console.ReadLine();
IsExist= DicObj.ContainsKey(index);
if (IsExist)
Console.Write("\nItem
Found!: \n");
else
Console.Write("\nItem Not
found!: \n");
}
//Search
Item by using Item Value
public void SearchByValue()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nEnter a
Item Value to Search");
item = Console.ReadLine();
IsExist = DicObj.ContainsValue(item);
if (IsExist)
Console.Write("\nItem
Found!: \n");
else
Console.Write("\nItem Not
found!: \n");
}
//
Display Items in the Dictionary
public void Display()
{
Console.Write("\nItems in the List are: \n");
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("\nKey" + " " + "value\n");
Console.Write("\n");
foreach( KeyValuePair<string, string> item in DicObj)
{
Console.Write(item.Key +" "+
item.Value);
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
}
}
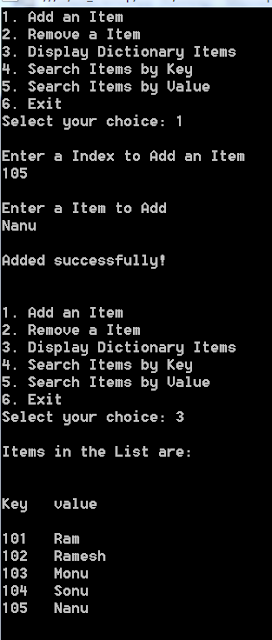
Output:-
Output Listing 2:-
Output Listing 3:-
Output Listing 4:-
Output Listing 5:-
Output Listing 6:-